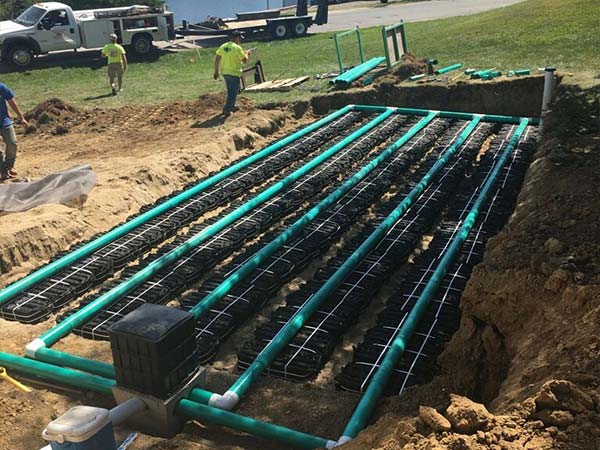
Residential Septic Systems
Traditional residential septic systems use leach fields and the underlying soil to help treat wastewater. Although this treatment process can be effective, it often contaminates the surrounding groundwater. Worse still, excessive buildup can clog nearby soil, which eventually causes the entire septic system to break down.
Passive Septic Systems
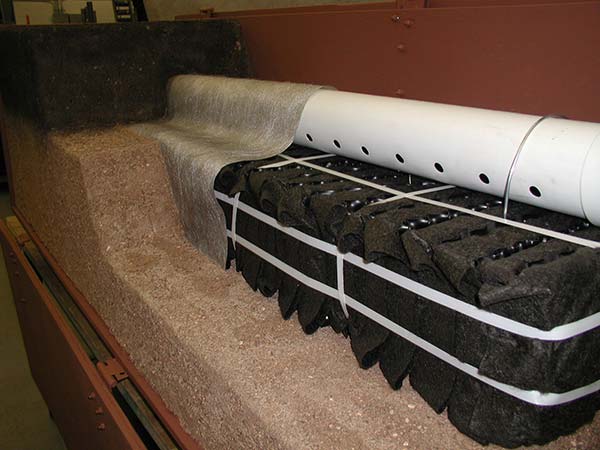
Eljen Geotextile Sand Filter (GSF)
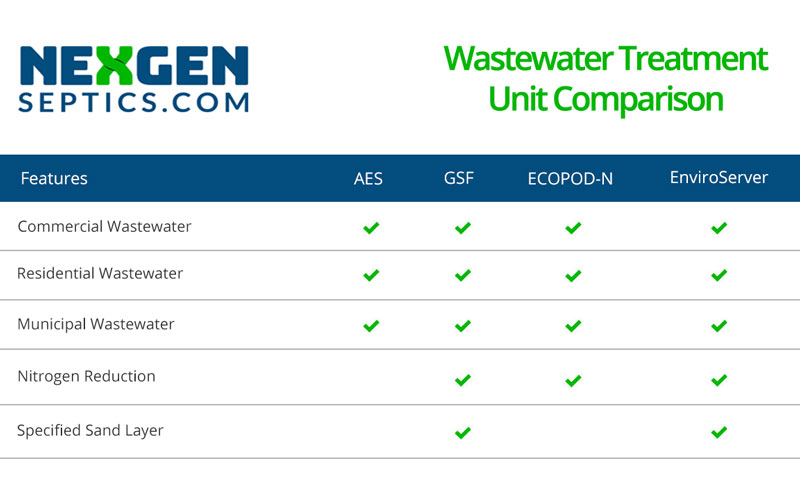
Geotextile fabric and plastic core materials function together to provide vertical surface area for biomat management and oxygen transfer in each GSF Module. In the GSF System, treated effluent is applied to the receiving soil, which increases soil acceptance. Additional filtration and dispersal is provided by the Specified Sand layer under and around the GSF units. This sand layer remains in an unsaturated state allowing for the free flow of effluent and beneficial bacteria.
Eljen Geotextile Sand Filter Key Features:
- Integrated treatment and dispersal
- Site installation flexibility
- Reduced impact on the site
- Easy to handle, lightweight
How the GSF System Works
In lieu of onsite septic leach field systems, Eljen offers its GSF (Geotextile Sand Filter). Testing performed by independent, third parties verifies the performance of the GSF under different conditions, but the system is composed of a primary treatment zone (containing the GSF Module) and a secondary treatment zone (Specified Sand layer). Over the GSF Module is a perforated pipe that distributes septic effluent into the corrugations created by the plastic core.
- The GSF Module is designed to manage the biomat and relieve the native soil of the burden of treatment and biomat development.
- Aerobic bacteria can grow on the GSF Module’s geotextile fabric interface thanks to open-air channels within the module. This promotes oxygen absorption in the system.
- The unique design of the GSF Module provides a large surface area for the biological treatment of contaminants and nutrients.
- The top and side sections of the Eljen GSF Module are covered with anti-siltation geotextile fabric to prevent fines from migrating into the open channels.
Secondary Wastewater Treatment
- As well as protecting the soil from compaction, Specified Sand acts as a filler, preventing cracks and crevices from appearing in the ground.
- The filtered effluent drips into the Specified Sand layer, with precise grain size allowing unsaturated flow into the surrounding native soil.
- The native soil serves as the final filtration layer and recharges the groundwater.
Specified Sand Layer
All Eljen GSF Systems must be installed using ASTM C33 sand that passes no more than 10% through a #100 sieve and no more than 5% through a #200 sieve to ensure that the system functions properly. This specification is the key to successful secondary treatment before the wastewater reenters the native soil.
Eljen (GSF)
Presby Enviro-Septic

- Both wastewater treatment and dispersal occupy the same small footprint.
- Both the soil and groundwater remain protected from effluent contamination.
However, the benefits of Enviro-Septic’s treatment technology go even further. Below are just some of the reasons why home owners throughout the country are increasingly turning to this popular water treatment alternative for their residential septic system.
Enviro-Septic® is an Affordable Residential Septic System
Thanks to its unique design, the Enviro-Septic® wastewater treatment system installs easily, helping to reduce many of the excavation and labor costs associated with replacing or upgrading older residential septic systems.
And because the entire system uses passive filtration:
- There are no mechanical devices, pumps, or crushed stones.
- There are no additives, chemicals, or replacement media.
Consequently, the Advanced Enviro-Septic® treatment technology is able to deliver superior results for a fraction of the cost.
Enviro-Septic® Residential Septic Systems Are Durable
With no mechanical moving parts, Enviro-Septic® enjoys an incredibly low failure rate. The system even has the ability to “rejuvenate” itself using its internal treatment technology.
This longevity helps to explain why Enviro-Septic® is already the “system of choice” in its home state of New Hampshire. And it also explains why this treatment solution is becoming so widespread throughout the United States.
Enviro-Septic® Pipe Is Versatile
The technology’s streamlined design allows for easy installation across a broad range of residential, commercial, or municipal applications. You can adapt this septic treatment system for:
- Flat or sloped lots.
- Rough or smooth terrain.
- Open areas or confined spaces.
Because the footprint is so compact, you can easily scale Enviro-Septic® systems for whatever projects you require.
Enviro-Septic® System Products Are Green
Unlike conventional leach field septic systems, Enviro-Septic® treats effluent before releasing wastewater into the surrounding soil. This helps to protect nearby aquifers, streams, and other endangered waterways that would normally become contaminated using less effective water treatment alternatives.
In fact, Enviro-Septic® currently exceeds the Environmental Protection Agency’s treatment standards for on-site septic systems, making it one of the greenest and most effective ways to treat contaminated wastewater.
Are Enviro-Septic® System Products Right for your Home?
With more than 20 years of proven experience in the field, the Enviro-Septic® system is one of the most powerful, durable, and cost-effective solutions for treating effluent. The fact that the system uses environmentally friendly filtration to remove up to 99% of contaminants which makes the Enviro-Septic product one of the greenest septic solutions on the market as well.
To learn more about how this passive treatment technology works, read our free owner’s manual here.
And if you’re looking for a replacement residential septic system, schedule a free consultation with us today.
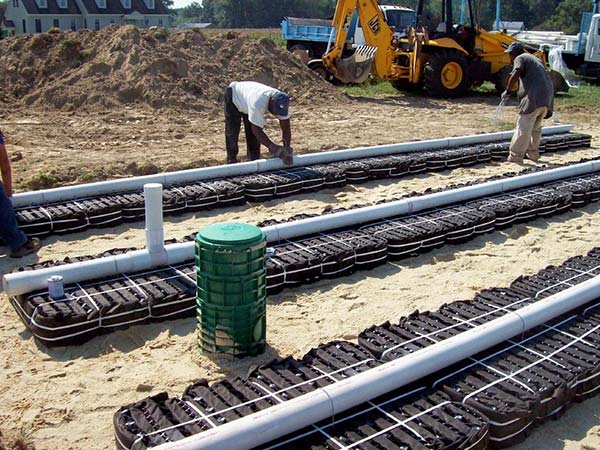
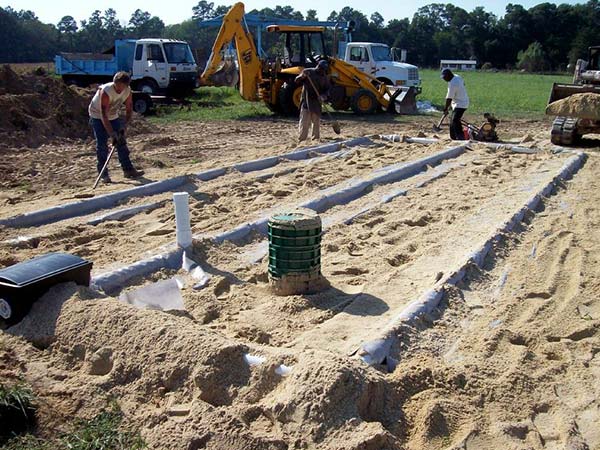
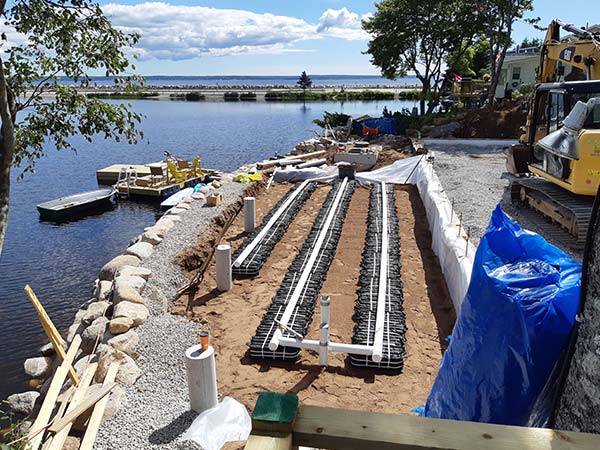
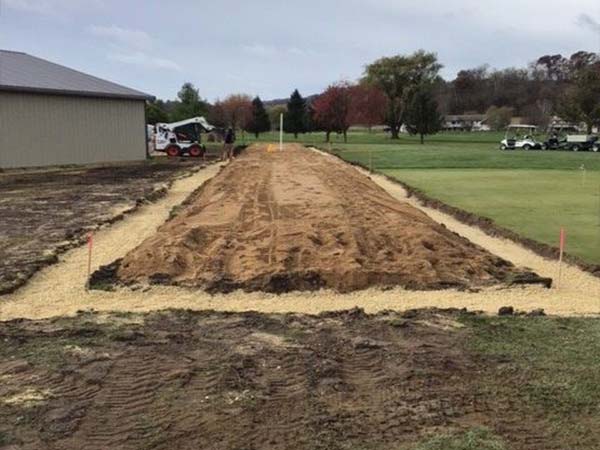
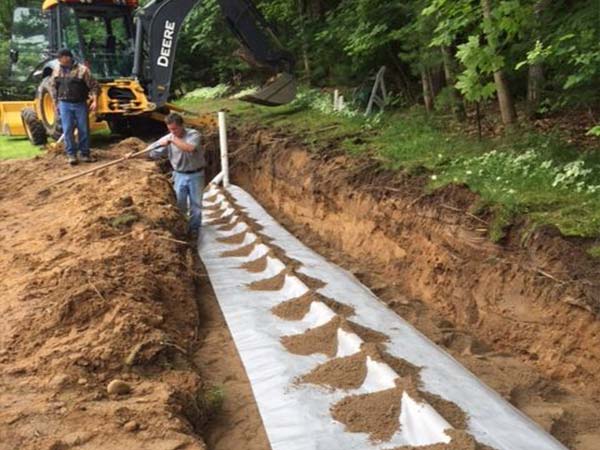
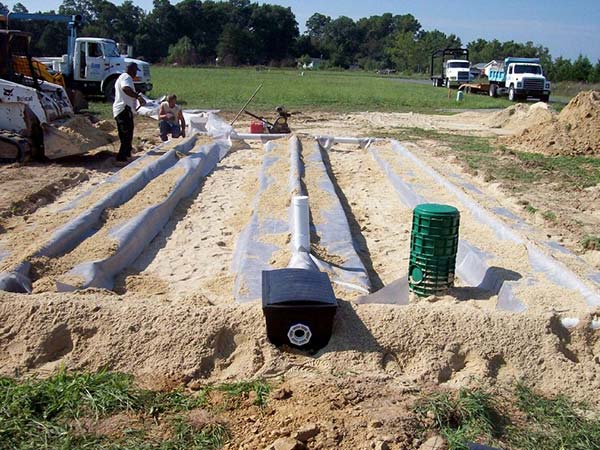
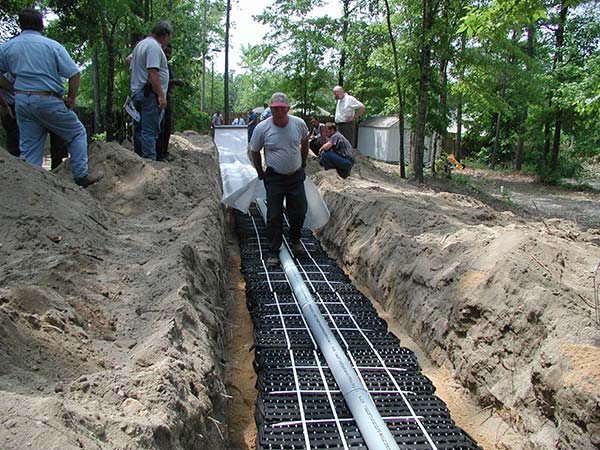
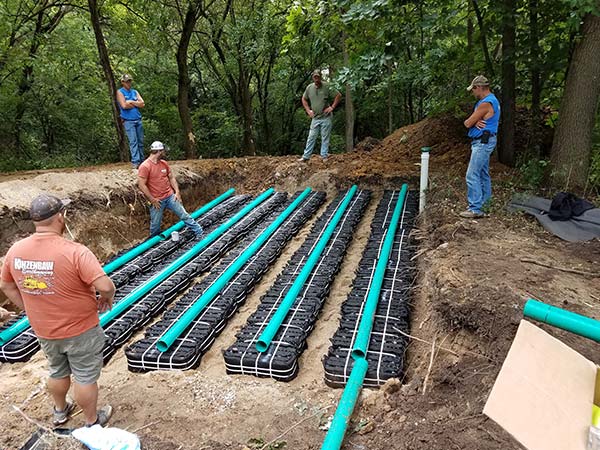
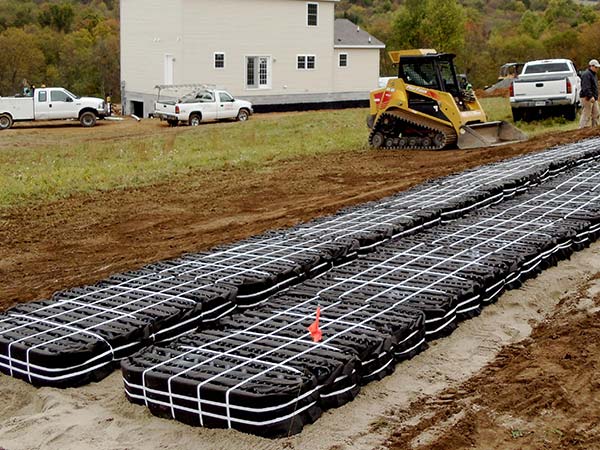
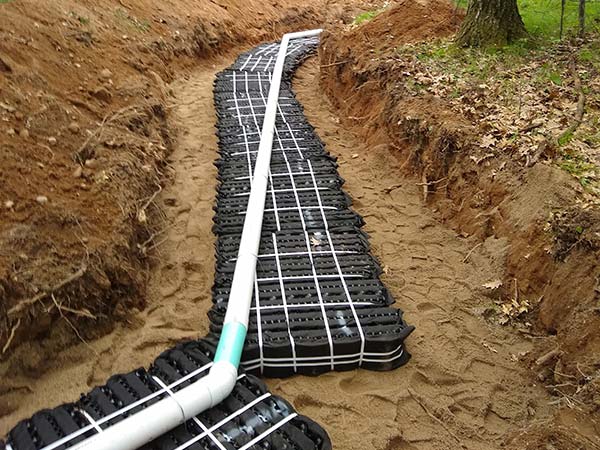
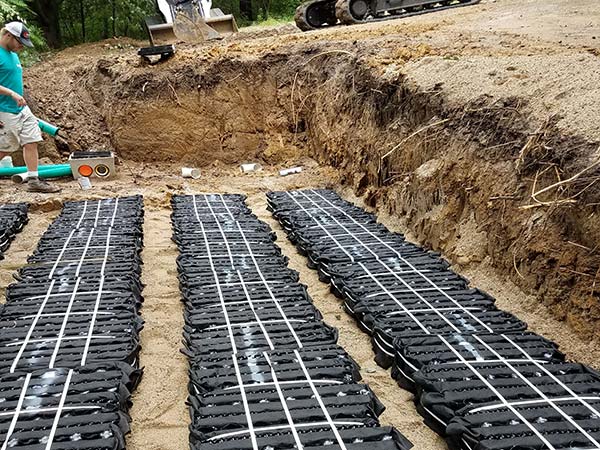
Advanced Enviro-Septic, Residential Septic System Gallery
Mechanical Treatment Systems
Delta ECOPOD-N
ECOPOD-N Advanced Wastewater Treatment Unit
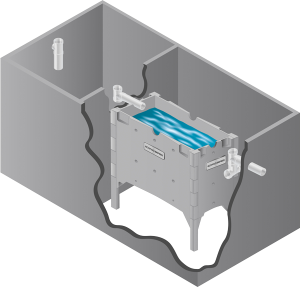
Delta ECOPOD-N Advanced Wastewater Treatment Unit Features:
• Oxygen is pumped into the system allowing the bacteria thrive and grow in much greater numbers than would occur naturally. This “overpopulation” of bacteria speeds the process of • breaking down the sewage, making it safe for release into the environment.
• ECOPOD-N units significantly reduce BOD, TSS, fecal coliforms, and nutrients in the wastewater.
• Nitrification and denitrification occur in a single tank.
• Features a fixed-film process which is characteristically stable, reliable and sturdy. Fixed-film is a preferred treatment process for onsite wastewater treatment systems.
MicroSeptic EnviroServer
Stage 1 – Primary Clarification
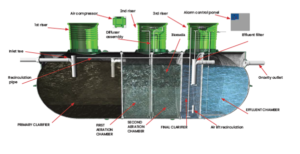
Stage 2 – Biological Organic Removal
In the second compartment, the wastewater is aerated using a high-efficiency, low-pressure air compressor and a fine-bubble membrane air diffuser assembly. The diffuser assembly is custom-designed to ensure maximum oxygen transfer and optimum mixing of dissolved substrates and oxygen. Furthermore, the mixing ensures the solids remain suspended within the reactor and the biomedia does not clog. The aeration promotes the growth of aerobic microorganisms, which convert and remove biodegradable organic matter. (The organics removed by the aerobic process are the constituents that are measured in the CBOD5 test.)

Stage 3 – Biological Ammonia Conversion (Nitrification)
The partially treated wastewater, now low in carbon but high in ammonia, flows into the third compartment (Second Aeration Chamber) of the system and is aerated in the same manner as the second compartment. The combination of low carbon content, high ammonia, and high oxygen levels in this chamber promotes the growth of nitrifying microorganisms (Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter). The nitrifying microorganisms convert ammonia to nitrates utilizing the oxygen in the wastewater.
Stage 4 – Clarification
The two-stage aerobically treated wastewater, which is now high in nitrates but low in carbon (BOD), flows into the fourth compartment (Final Clarifier) of the system where clarification and settling of suspended solids occurs.
Stage 5 – Nitrate Removal
To promote denitrification, the wastewater is recirculated from the final clarifier back to the primary clarifier, which contains enough carbon to promote denitrification. Denitrification occurs because the bacteria in the primary (anoxic) clarifier use the oxygen from the nitrate molecules in their metabolic process; the nitrogen left over from this reaction is then released as a gas.
Stage 6 – Solids Removal

Because of the recirculation, the sludge is accumulated and stored in the primary clarifier. The primary clarifier is sized to hold sludge for one to three years, depending on the usage of the system, and pumping is required as needed.
Stage 7 – Effluent Filtration and Disinfection (optional)
The clarified water leaves the treatment compartments through an effluent filter into the final storage compartment (Effluent Chamber). The effluent filter protects the effluent chamber and subsequent dispersal field from solids carry-over during upset conditions. It is designed to remove all particles larger than 1/16”. An UV-disinfection unit can be added to sterilize remaining pathogens, including fecal coliform. When selected, the clarified water passes through a disinfection unit after it leaves the effluent filter. The effluent is now ready for discharge.
Save 10% on All Septic Products
For All New Customers
"*" indicates required fields